But there are some sexual contexts that can increase your risk of getting a UTI. The reason that individuals need to understand the difference between a UTI and an STI is twofold.

There is no sign or symptom of the STDSTI virus present inside the body.
Sti vs uti. STIs can feel similar to a UTI because the infection can often be felt as burning pain upon urination and pelvic pain Dr. Sheila Loanzon an OBGYN and author of Yes I Have Herpes. The difference between STI and UTI.
A Sexually Transmissible Infection STI is an infection that can be passed on through vaginal anal or oral sex. Most STIs are transmitted through the exchange of sexual fluids but some can be passed on through skin to skin genital contact. These are perfectly normal thoughts that may go through your head before seeing a doctor for a potential urinary tract infection UTI or sexually transmitted infection STI.
UTI and what is the difference between their symptoms are quite a common dilemma. There are some symptoms similar to both a Sexually Transmitted Infection STI and a Urinary Tract Infection UTI so sometimes it may be difficult to discern which type of infection your symptoms represent. What follows may help you to spot the difference quickly and take action.
Its easy to see why people get confused when it comes to urinary tract infections UTI and sexually transmitted infections STIs. After all both involve genitals and they can share some similar symptoms. But its important you understand the difference so that you know when its time to.
You see a UTI is an infection in your urinary tract that can be caused during sex. However it has more possible causes than sex. An STI on the other hand is a sexually transmitted disease that almost always requires sex to getthat is an infection transmitted from one person to another through sexual activity.
UTIs and STDs share very common symptoms and are misdiagnosed more often than you may think. According to the American Society for Microbiology 64 percent of the patients with an STI sexually transmitted infection were actually diagnosed as having a UTI instead. Not only are women being needlessly prescribed a UTI treatment which can lead to antibiotic resistance.
The reason that individuals need to understand the difference between a UTI and an STI is twofold. First UTIs are often treated with a round of a specific type of antibiotics. Treating with these when there is no urinary tract infection is pointless but can also lead to the body becoming resistant to the strain of antibiotics.
Note that lower tract UTI affects bladder and urethra whereas the upper tract UTI cause problem to kidneys. The second type upper tract UTI is more dangerous as it may cause transfer of bacteria from the kidney to blood. This health condition is named as urosepsis and it can further lead to shock low blood pressure and even death.
The symptoms of upper tract UTI includes vomiting nausea fever. Although there are common symptoms between STI and UTI such as painful or difficult urination frequent urination or the urge to urinate as well as urine that is cloudy dark or has a strange smell etc. With STD it is mostly asymptomatic ie.
There is no sign or symptom of the STDSTI virus present inside the body. UTI and what is the difference between their symptoms is quite a common dilemma. There are some symptoms similar to both a Sexually Transmitted Infection STI and a Urinary Tract Infection UTI so sometimes it may be difficult to to discern which type of infection your symptoms represent.
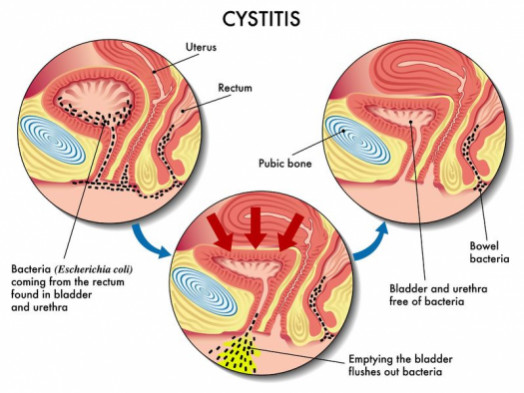
UTI-caused cystitis may be called bacterial cystitis or bladder infection. Or painful bladder syndrome is non-infectious cystitis caused by chronic inflammation in the bladder. Both interstitial cystitis and UTI are more common in women than men.
They both share similar symptoms. While UTIs and STDs have some symptoms in common there are also differences that can give you clues about the most likely cause. What is a UTI.
In a urinary tract infection also known as a UTI bacteria infect any part of the urinary tract which consists of the urethra bladder ureter and kidneys. Sixty 23 of the 264 women studied had one or more positive STI tests 22 37 of whom did not receive treatment for an STI within 7 days of the ED visit. Fourteen 64 of these 22 women were diagnosed with a UTI instead of an STI.
Ninety-two percent of the women studied had an abnormal UA finding greater-than-trace leukocyte esterase level positive nitrite test result or pyuria. Unlike a sexually transmitted disease a UTI cannot be transmitted via sexual or non-sexual contact. But there are some sexual contexts that can increase your risk of getting a UTI.
Not urinating after having sex is a good example. As mentioned above STDs and UTIs can often have symptoms similar to each other. A urinary tract infection or UTI refers to a bacterial infection in any part of your urinary system including the urethra bladder ureters and kidneys.
Most UTIs affect the lower urinary tract comprising the urethra and bladder. UTIs can become more severe as they reach the kidneys. UTI and what is the difference between their symptoms is quite a common dilemma.
There are some symptoms similar to both a Sexually Transmitted Infection STI and a Urinary Tract Infection UTI so sometimes it may be difficult to to discern which type of infection your symptoms representWhat follows may help you to spot the difference quickly and take action. UTI or STD. How to Tell the Difference.
The symptoms of many common STDs can cross over and be similar to if you have a UTI.